说明 - 2022-05-05
本篇博客为本人原创, 原发布于CSDN, 在搭建个人博客后使用爬虫批量爬取并挂到个人博客, 出于一些技术原因博客未能完全还原到初始版本(而且我懒得修改), 在观看体验上会有一些瑕疵 ,若有需求会发布重制版总结性新博客。发布时间统一定为1111年11月11日。钦此。
讨论的内容如题
分析
拿中序遍历和后序遍历的组合举例子
设数组last[]储存后续遍历 in[]中序遍历,它们的长度都是n(数组从1开始计,下标范围是1-n)
树根自然为last[n]
,这时我们遍历in[]数组,在in[]数组中找到last[n]的值的下标idx,因为in[]储存的是中序遍历,显然我们以idx为界把in数组的序列分成两份[1,idx-1],[idx+1,n],分别为两颗子树上的节点。
之后我们便可以在分出的两个区间之中重复上述操作,分别找目前子树的根节点,再二分区间,直到获得完整的二叉树
可以使用递归来完成 函数(区间左,区间右,根节点,偏移量)
此时注意一个问题:当区间被二分之后,我们发现后面的区间在in[]数组和last[]数组中的下标“对不齐”了,即下标发生了偏移,如下图。所以要引入一个变量shift来记录偏移量。(偏移量最开始是0,递归时前面的区间继承原偏移量,后面的区间偏移量为原偏移量+1)
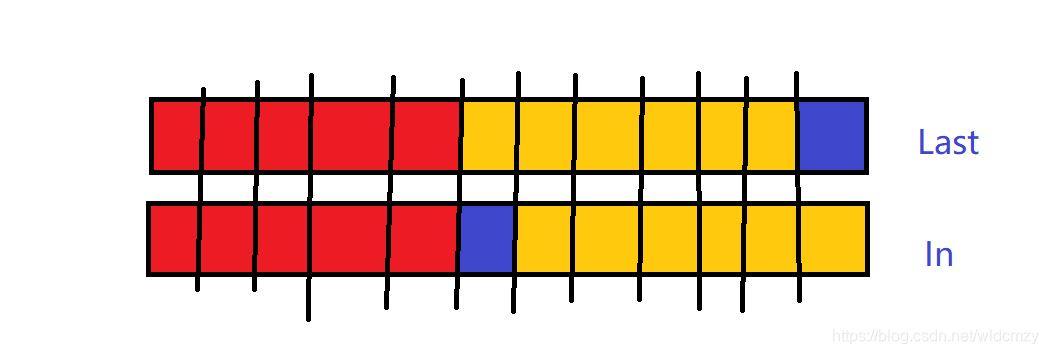
(在前序遍历和中序遍历的组合中,下标发生偏移的是前面的区间)
例题 后序遍历和中序遍历的组合
https://vjudge.net/contest/386054#problem/E
#include
#include
#include
struct Node
{
int l,r;
};
Node treeN[10010];
int inorder[10010],postorder[10010];
int len,rt,least,lstPos;
int input()//返回数组长度
{
int n,idx=1;
char ch;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
inorder[idx++]=n;
ch=getchar();
if(ch==’\n’)
break;
}
idx=1;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
postorder[idx++]=n;
ch=getchar();
if(ch==’\n’)
break;
}
return idx-1;
}
int makeTree(int l,int r,int root,int n)
{
if(l>r)
return -1;
int idx=-1;
for(int i=l; i<=r; i++)
{
if(inorder[i]root)
{
idx=i;
break;
}
}
if(idx>0)
{
treeN[root].l=makeTree(l,idx-1,postorder[idx-n-1],n);
treeN[root].r=makeTree(idx+1,r,postorder[r-n-1],n+1);
}
return root;
}
void add(int root,int base)
{
int total=base+root;
if(treeN[root].l-1 && treeN[root].r==-1)
{
if(lstPos==-1)
{
least=total;
lstPos=root;
}
else
{
if(total<least)
{
least=total;
lstPos=root;
}
}
return ;
}
if(treeN[root].l>0)
{
add(treeN[root].l,total);
}
if(treeN[root].r>0)
{
add(treeN[root].r,total);
}
}
int main()
{
while((len=input())>0)
{
memset(treeN,-1,sizeof(treeN));
lstPos=-1;
rt=makeTree(1,len,postorder[len],0);
add(rt,0);
std::cout << lstPos << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
例题 前序遍历和中序遍历的组合
<https://pintia.cn/problem-
sets/1303281293857476608/problems/1303281404742291466>
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
const int N=32;
int n;
struct Node
{
int l,r;
}treeN[N];
int pre[N],in[N];
int fff(int root,int l,int r,int shift)
{
if(l>r) return -1;
int i;
for(i=l; i<=r; i++) if(root==in[i]) break;
if(i<=r)
{
treeN[root].l=fff(pre[l+1+shift],l,i-1,shift+1);
treeN[root].r=fff(pre[i+1+shift],i+1,r,shift);
}
return root;
}
void rev(int root)
{
if(root==0) return ;
treeN[root].r=treeN[root].r^treeN[root].l;
treeN[root].l=treeN[root].r^treeN[root].l;
treeN[root].r=treeN[root].r^treeN[root].l;
rev(treeN[root].l);
rev(treeN[root].r);
}
void gogogo(int root)
{
std::queue<int >q;
std::cout << root;
if(treeN[root].l!=-1) q.push(treeN[root].l);
if(treeN[root].r!=-1) q.push(treeN[root].r);
while(!q.empty())
{
root=q.front(); q.pop();
std::cout << " " << root;
if(treeN[root].l!=-1) q.push(treeN[root].l);
if(treeN[root].r!=-1) q.push(treeN[root].r);
}
}
int main()
{
std::cin >> n;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) std::cin >> in[i];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) std::cin >> pre[i];
int root=fff(pre[0],0,n-1,0);
rev(root);
gogogo(root);
return 0;
}